Author: admin

Japan Takes Center Stage in Microbiota Innovation
Tokyo to Host Global Summit Showcasing the Nation’s Leadership in Fermentation Science and Microbiome Medicine Japan is reinforcing its position as a global powerhouse in microbiota research and fermentation science, as the country prepares to host the First Conjoint Meeting ISM–RIKEN – Targeting Microbiota this October in Tokyo. Long recognized for its centuries-old Fermentation…

Short Orals & Poster Communications Accepted
Short Oral Accepted Metabolic Profiling and Mining of Microbiota by Raman Flow Cytometry and Single-cell RACS-seq/culture Jian Xu, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology, China Faecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Method of Treatment of Different Etiologies of Intestinal Syndrome in Children Julia Bespyatykh, Lopukhin Federal Research and Clinical Center…

Good Bacteria on Our Skin May Help Protect Us from Sun Damage
A new study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology shows that some of the bacteria naturally living on our skin can help protect us from the harmful effects of sunlight. What Did Scientists Discover? When our skin is exposed to UVB rays from the sun, it produces a molecule called cis-urocanic acid,…
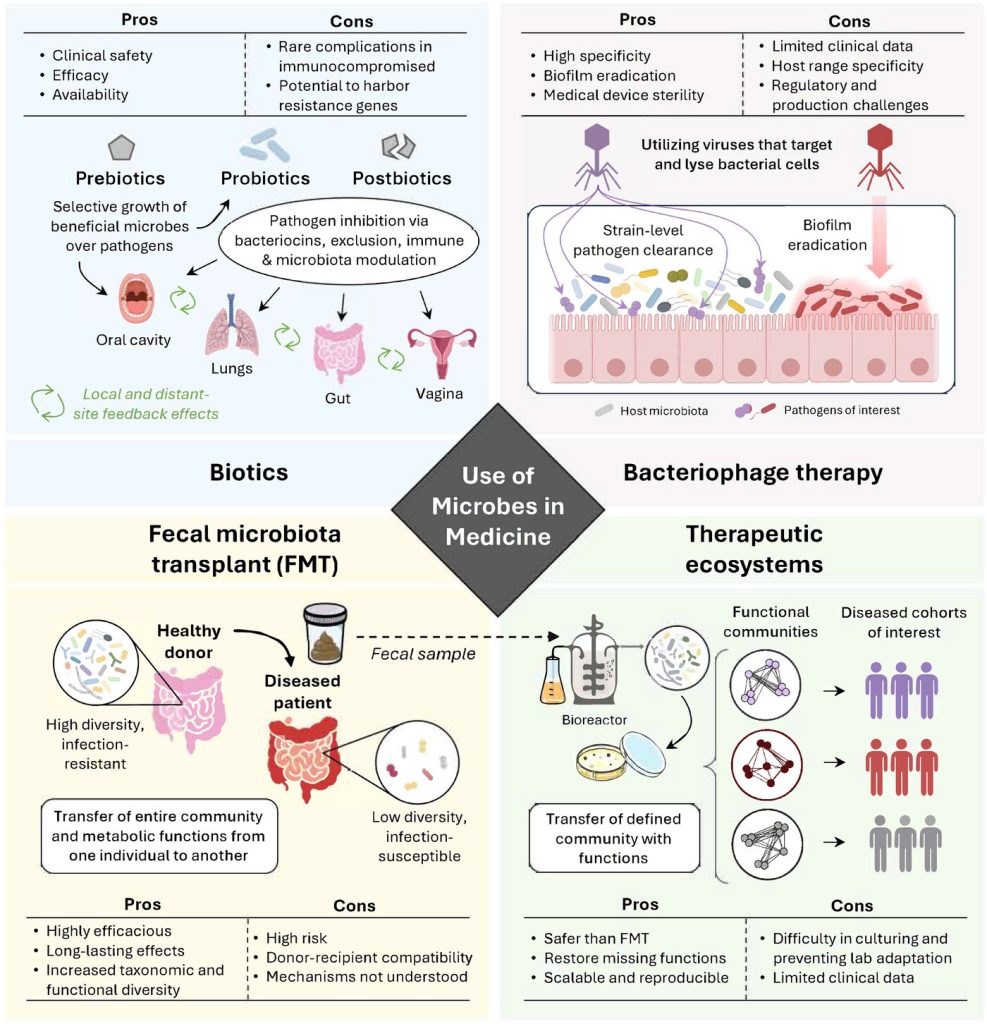
The Microbiome Revolution: Personalized Therapies for a Healthier Future
The human microbiome is a critical component of overall health, influencing digestion, immunity, and even mental well-being. Advances in research have highlighted the importance of maintaining microbial diversity and developing targeted therapies to restore balance. With the increasing concern over antibiotic resistance and chronic diseases linked to microbiome disruption, scientists are exploring innovative strategies, including…
Altered Gut Microbiota, Reduced Butyrate, and Increased Gray Matter Free Water in Alzheimer’s and MCI Patients
A study published in Neurobiology of Disease () investigated the link between neuroinflammation, gut microbiota changes, and butyrate depletion in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Neuroinflammation plays a key role in AD progression, and free water (FW) imaging, which measures extracellular water content, serves as a marker for this process.…

Brewing Gut Health How Coffee Consumption Shapes the Microbiome and Boosts Beneficial Bacteria
A recent study published in Nature Microbiology explores the relationship between coffee consumption and the human gut microbiome. Researchers found a significant association between coffee intake and the presence of Lawsonibacter asaccharolyticus, a bacterial species recently isolated from the human intestine (Nature Microbiology, 2024). Key Findings Association with Lawsonibacter asaccharolyticus: Higher coffee consumption correlates with…

Barley and Natto Consumption Linked to Beneficial Gut Bacteria in Non-Obese Individuals
A recent study led by Jun Kunisawa from the National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Japan, explores the relationship between high barley consumption, natto intake, and gut microbiota composition in non-obese individuals. Barley, rich in β-glucan, is known for its potential role in obesity prevention. Since dietary fiber is metabolized by gut microbiota, researchers investigated the…
