Prof. Marvin Edeas and his team presented a study on Intelligence Artificial and Health meeting at University Paris-Sud
The Intelligence Artificial and Health meeting was held on November 25, 2019, at University Paris-Sud. During the meeting, Prof. Marvin Edeas from INSERM - U1016, Institut Cochin, Hôpital Cochin, University Paris Descartes with his team presented a study entitled "Artificial Intelligence in the Healthcare Industry: The Hemodialysis patients with cramps initiative".
Introduction
Artificial intelligence in the healthcare industry will open a huge opportunity. Demand for basic and advanced analytics is growing exponentially in healthcare. We are beginning to enter into an era where life sciences and data science are merging. Our initiative will collect clinical data from hemodialysis patients, which will urgently need a Data Scientists to process it. To be able to analyze and make recommendations based on this data, we need AI.
Methods
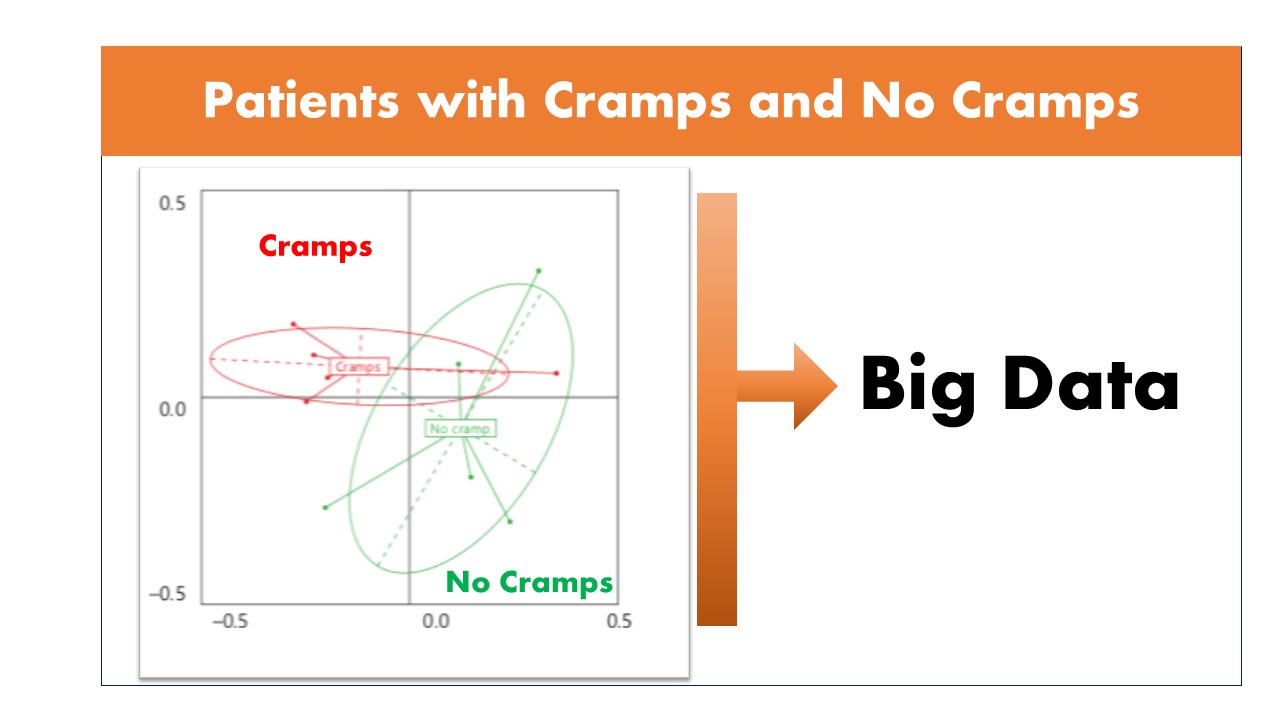
For the first time we published in 2018 a possible link between Microbiota quality, mitochondrial activity and the occurrence of muscle cramps in hemodialysis patients using citrate dialysate. Our objectives were to assess the gut microbiota quality, mitochondrial activity, and to investigate their possible relationship with HD-associated muscle cramp (HDAMC). This clinical study revealed a possible dysbiosis of microbiota and mitochondrial dysfunction in HD patients with cramps under CD compared to patients without cramp.
Confirmation of our observations is required in a large-scale study, which could demonstrate a novel pathophysiological mechanism linking muscle cramps to gut microbiota HD patients. We now have a cohort of more than 1500 patients to complete our study.
Results Expected
We will use a combined microbiome and metabolome signatures in feces and metabolome in plasma as new biomarkers to identify in upstream the HD patients with altered metabolism in order to propose an adapted therapy. Advances in sequencing technologies could provide opportunities to understand not only the taxonomy but also the functional diversity of gut microbiota. These investigations could allow to justify the use of antibiotics, probiotics, prebiotics, or fecal microbiota transplantation to modulate gut microbiota as curatives or preventive strategies of muscle cramps. We will also look for a predictive marker of muscle cramps by initiating an Artificial Intelligence program.
Conclusion
There are significant hurdles to be overcome with our hemodialysis initiative: 1-finding talented data scientists. 2- regulatory aspects. This presentation will address these considerations.
Durand, P.-Y., Nicco, C., Serteyn, D., Attaf, D. & Edeas, M. Microbiota Quality and Mitochondrial Activity Link with Occurrence of Muscle Cramps in Hemodialysis Patients using Citrate Dialysate: A Pilot Study.
Blood Purif. 46, 301–308 (2018).
For more info, please check the agenda here: http://www.medecine.u-psud.fr/fr/recherche/colloque-intelligence-artificielle-et-sante.html