Butyrate and Gut Health: Advances in Clinical Applications
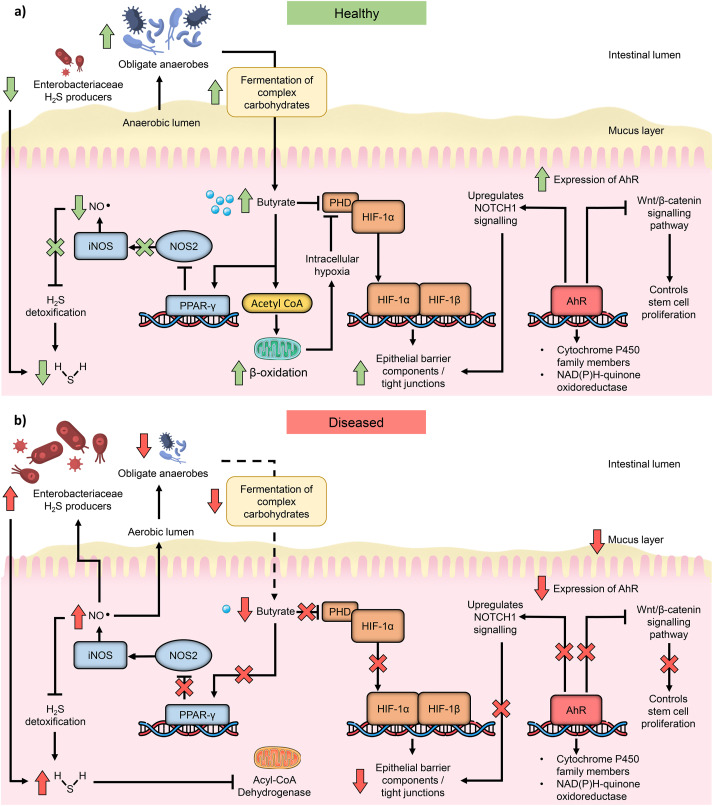
Microbial-derived butyrate modulates intestinal epithelial immunometabolic circuitry to maintain gut homeostasis.
Butyrate, a key metabolite produced by gut microbiota through the fermentation of dietary fiber, plays a crucial role in maintaining gastrointestinal health. Researchers from the University of Ottawa, Canada, highlight its impact on colonocyte function, gut barrier integrity, and inflammation control.
Beyond serving as an energy source, butyrate acts as a histone deacetylase inhibitor and signals through G-protein coupled receptors, influencing both host and microbial functions. Studies suggest its protective role against inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), graft-versus-host disease, and colon cancer. However, clinical efforts to enhance butyrate levels have yielded mixed results, highlighting the complexity of microbiota-host interactions.
This research provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of butyrate action and ongoing efforts to translate these findings into therapeutic strategies. Understanding the delicate balance between microbiota-derived metabolites and human health is essential for advancing microbiome-based interventions.
Image Credits: Hodgkinson, Kendra et al. Clinical Nutrition (2023)