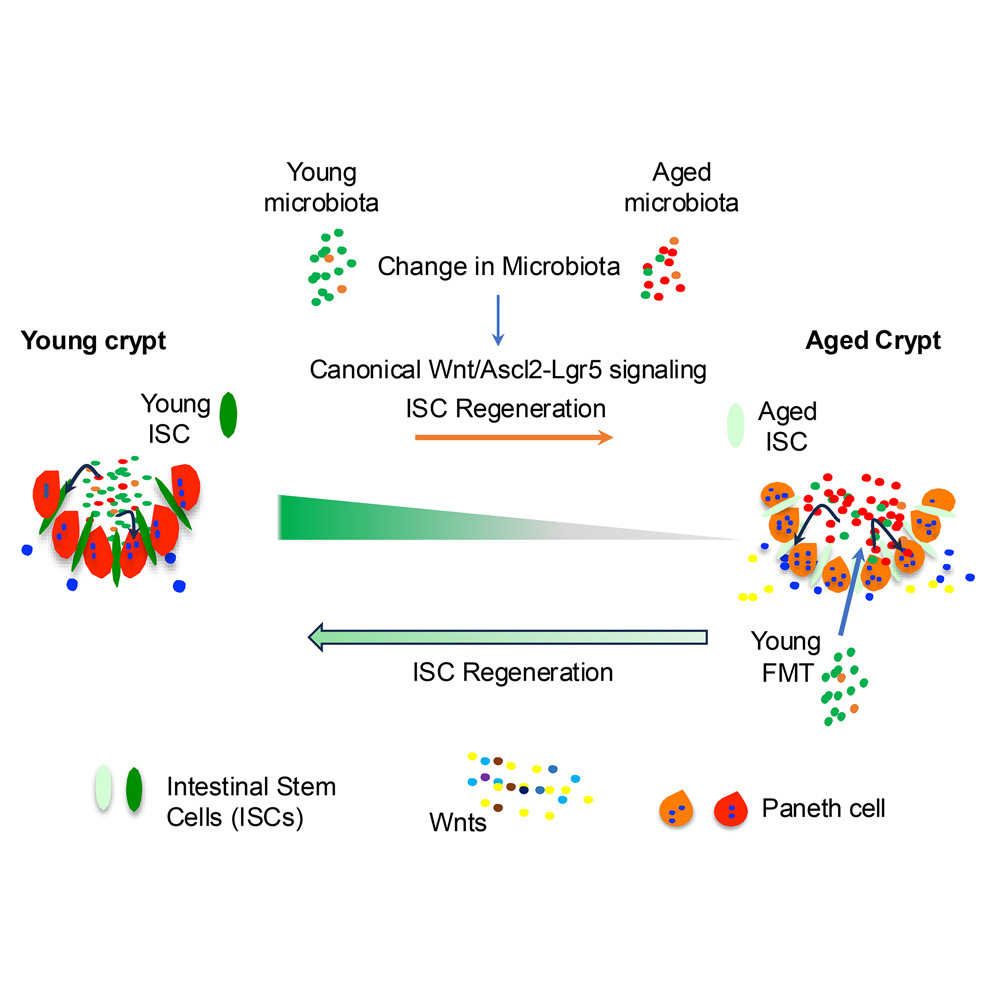
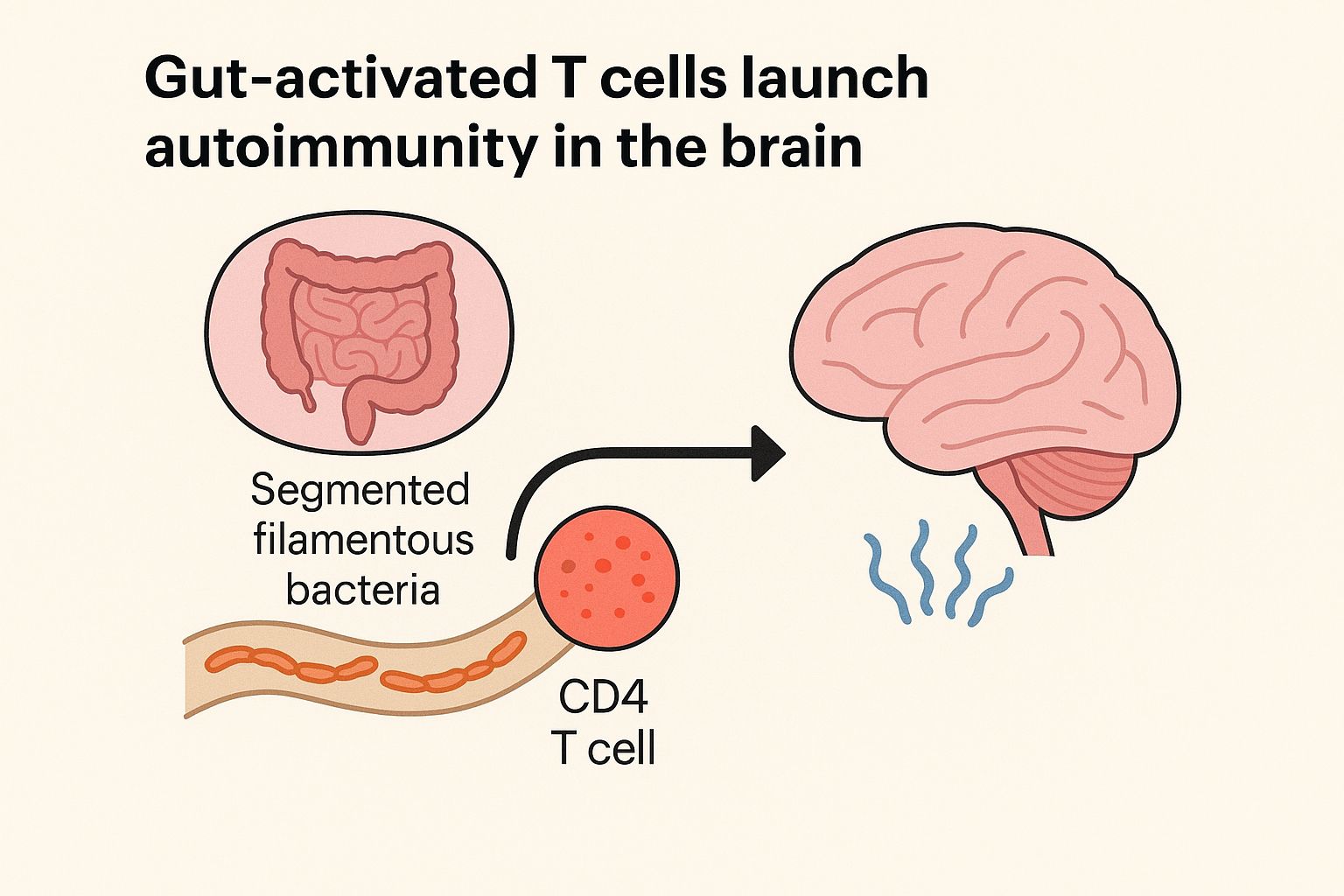
A research team from the University of Chicago has created a new computational high-throughput RNA sequencing strategy that will provide insights into the activity of gut microbiome like never before.
“Advances in high-throughput sequencing have facilitated remarkable insights into the diversity and functioning of naturally occurring microbes; however, current sequencing strategies are insufficient to reveal physiological states of microbial communities associated with protein translation dynamics. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are core components of protein synthesis machinery, present in all living cells, and are phylogenetically tractable, which make them ideal targets to gain physiological insights into environmental microbes. Here we report a direct sequencing approach, tRNA-seq, and a software suite, tRNA-seq-tools, to recover sequences, abundance profiles, and post-transcriptional modifications of microbial tRNA transcripts. Our analysis of cecal samples using tRNA-seq distinguishes high-fat- and low-fat-fed mice in a comparable fashion to 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicons, and reveals taxon- and diet-dependent variations in tRNA modifications. Our results provide taxon-specific in situ insights into the dynamics of tRNA gene expression and post-transcriptional modifications within complex environmental microbiomes.”