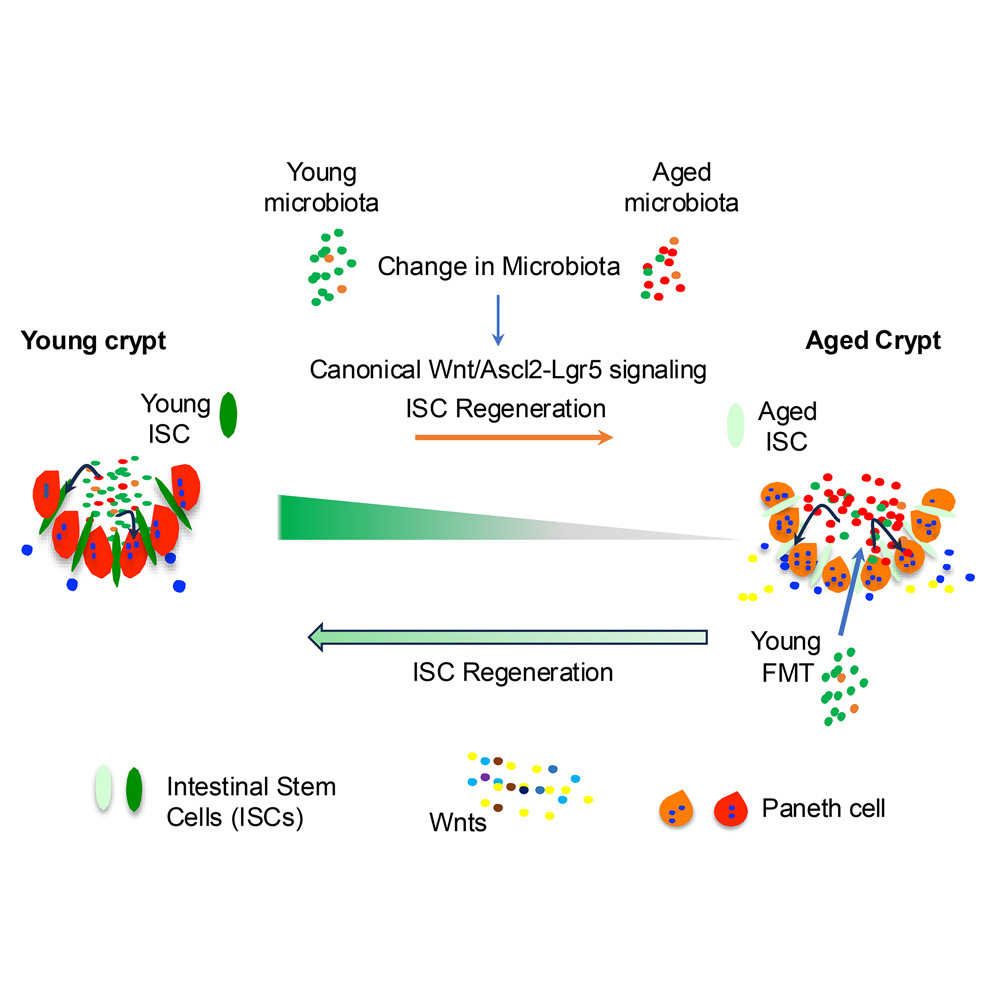
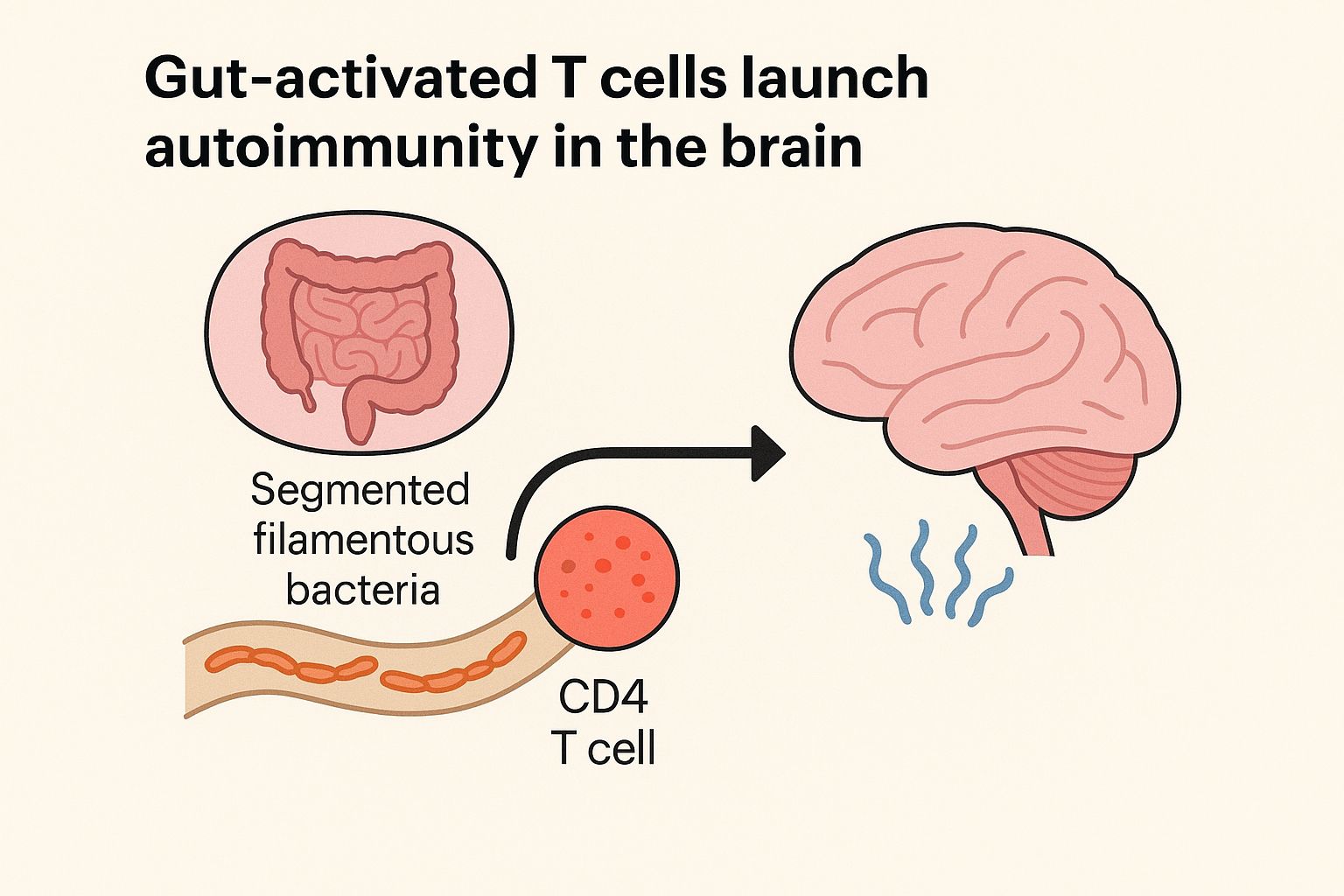
Gut Microbiota Composition Reflects Disease Severity and Dysfunctional Immune Responses in Patients with COVID-19
The Scope is: Although COVID-19 is primarily a respiratory illness, there is mounting evidence suggesting that the GI tract is involved in this disease. We investigated whether the gut microbiome is linked to disease severity in patients with COVID-19, and whether perturbations in microbiome composition, if any, resolve with clearance of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
To Conclude: Associations between gut microbiota composition, levels of cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19 suggest that the gut microbiome is involved in the magnitude of COVID-19 severity possibly via modulating host immune responses. Furthermore, the gut microbiota dysbiosis after disease resolution could contribute to persistent symptoms, highlighting a need to understand how gut microorganisms are involved in inflammation and COVID-19.
Full Article: https://gut.bmj.com/content/70/4/698
This topic will be discussed by Prof. Siew C Ngwill during the World Congress on Targeting Microbiota 2021 which will be held on October 20-22, 2021.
Targeting Microbiota 2021 Congress
October 20-22, 2021
www.microbiota-site.com